January 29, 2024
Solar Farm Siting
Solar Farm Site Analysis
One of the most important factors contributing to the success of a solar farm is the location. Identifying suitable locations quickly and reliably is the key to getting ahead in an increasingly competitive market. Developers need to eliminate non-viable sites quickly in order to focus their efforts on closing deals on the sites that matter. As part of site identification, developers look at a variety of factors which all impact the potential finances of a solar project and will ultimately guide the decision on whether to move forward with a solar farm at a specific location.
The Site Selection Process
In order to choose a site suitable for a solar farm, developers need to evaluate sites based on a variety of criteria.
Grid Infrastructure
One of the best places to start is with grid infrastructure. A solar farm needs to be connected to the grid to deliver energy, and interconnection costs can make or break a project. Choosing sites close to transmission lines, distribution lines, and substations helps minimize interconnection costs. Asking the utility to run miles of generation tie lines will add millions in costs and significant delays to a project.
Land assessment
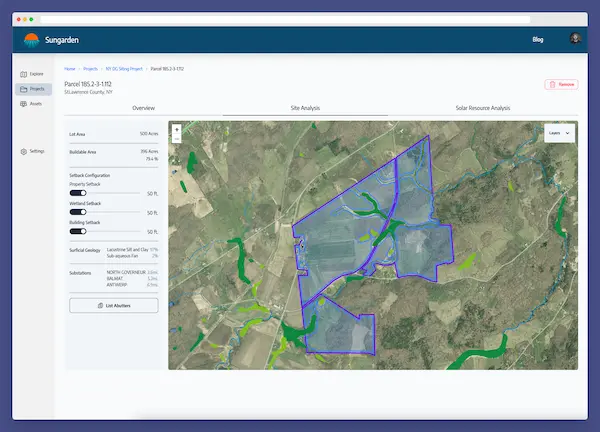
Given the availability of nearby transmission or distribution infrastructure, developers will look for suitable parcels of land on which to build the farm. The ideal property is accessible by construction and maintenance vehicles, relatively flat, and clear. Developers don't want to clear densely wooded land, or do expensive cut and fill to level a property. The necessary property size varies with the size of the farm being built. Solar farms generally need between 6 and 9 acres per Megawatt of capacity. Along with these criteria, solar developers need to consider environmental factors, such as floodplains, wetlands, and endangered species' habitats.
Solar Resource Analysis
Developers need to choose sites that have adequate solar potential. Developers will look at historical data to get a sense of the typical weather conditions and solar irradiance at a given location. Generally they'll use hourly values to get a detailed sense of how the farm will perform throughout the year. In addition to the available irradiance, solar production can be affected by local weather conditions, ground type, and topology. Snow and dirt can prevent panels from operating efficiently, and shadows from trees, terrain, and buildings can cause reduced production as well as maintenance issues. Developers need to take all of this into account when choosing a site for their solar farm.
Community
Another important thing to keep in mind is the community that the solar farm will be built in. This is important for several reasons. The Inflation Reduction Act provides Interconnection tax credits for projects built in low income and "energy" communities, which makes some areas more enticing than others. In addition, understanding community concerns and what it takes to address them can help avoid a drawn-out permitting and approval processes.
Regulatory Compliance
It's important to have an understanding of local and statewide programs and regulations when considering a solar farm. Things like capacity limits, property setbacks, and more can impact the needs of a particular project.
Site Selection Solutions
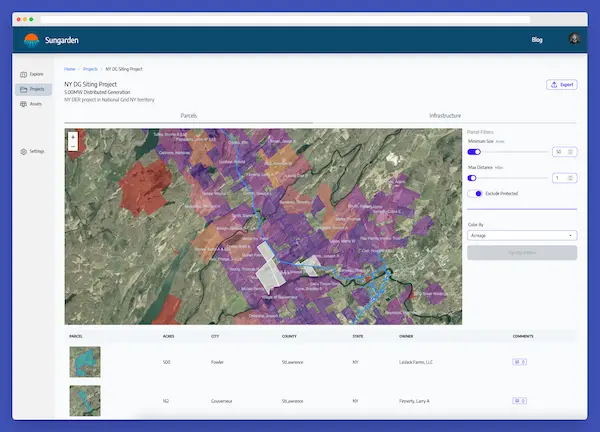 Using a tool like Sungarden gives solar developers immediate access to nearly all of this information, which helps them
zero in on
feasible sites quickly. Combining available layers such as utility infrastructure, tax credit availability, wetlands,
floodplains, conservation lands, and parcel size into search criteria lets developers find potential sites in seconds.
Once the search is narrowed down, developers can do detailed analyses of properties to identify any potential issues.
Using a tool like Sungarden gives solar developers immediate access to nearly all of this information, which helps them
zero in on
feasible sites quickly. Combining available layers such as utility infrastructure, tax credit availability, wetlands,
floodplains, conservation lands, and parcel size into search criteria lets developers find potential sites in seconds.
Once the search is narrowed down, developers can do detailed analyses of properties to identify any potential issues.